热线电话:0755-23712116
邮箱:contact@shuangyi-tech.com
地址:深圳市宝安区沙井街道后亭茅洲山工业园工业大厦全至科技创新园科创大厦2层2A
CCD视觉基础知识要点
1. 图像系统方案
光源选型模拟方案(针对物体速度比较慢)
组成:模拟相机,镜头,图像(视频)采集卡,光源和图像处理软件,数字方案(针对物体速度比较快)
组成:数字相机,镜头,图像转接卡,光源和图像处理软件
对特定的检测目标首先要确认目标物的性质:视野、物距、精度、运动方式(静止或者运动)、物体形状(考虑圆柱形物体用线阵摄像头)
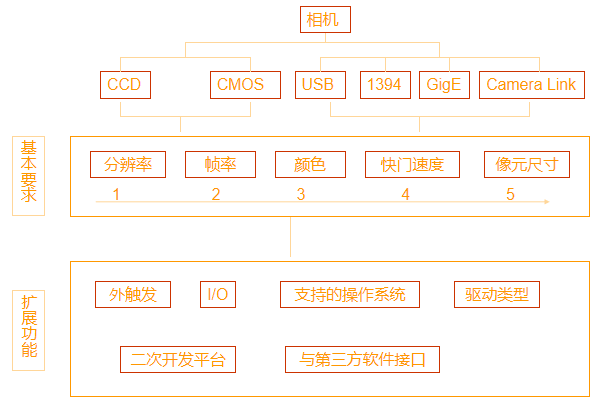
感光芯片类型:
A. COMS(互补金属氧化物半导体)
B. CCD(电荷耦合器件)
芯片主要参数:
A.分辨率和像元尺寸
640*480;1024*768;1280*960
1英寸 ——靶面尺寸为宽12.7mm×高9.6mm,对角线16mm
2/3英寸——靶面尺寸为宽8.8mm×高6.6mm,对角线11mm
1/2英寸——靶面尺寸为宽6.4mm×高4.8mm,对角线8mm
1/3英寸——靶面尺寸为宽4.8mm×高3.6mm,对角线6mm
1/4英寸——靶面尺寸为宽3.2mm×高2.4mm,对角线4mm
B.帧率(fps) 常见CCD帧率 15fps;30fps;60fps
C.颜色 灰度和彩色(Bayer和3CCD)
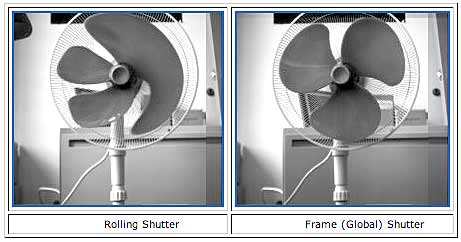
D.快门速度 1/10000s,1/50000s 快门方式:全局和卷帘
A. GLOBAL SHUTTER exposes the entire imager simultaneously. The entire frame is exposed and begins gathering light; when the predetermined “shutter speed” has elapsed, the sensor stops gathering light and turns its current exposure into an electronic image. There is no physical “shutter” that covers and uncovers the sensor; it’s all done with timing. At the start of exposure the entire sensor starts gathering light; at the end of exposure the light-gathering circuitry is turned off and the contents of the sensor are then “read out” to become an image.
A. ROLLING SHUTTER is very different. The rolling shutter actually exposes different portions of the frame at different points in time, “rolling” through the frame. Again, it’s not an actual physical moving shutter that’s doing this (as opposed to a movie camera, which actually has a moving physical shutter). Instead, the sensor is telling different portions to become light-sensitive at different moments in time, and as this process proceeds down the course of the full frame, until the entire frame is exposed.
http://dvxuser.com/jason/CMOS-CCD/
快门速度计算:
假设速度是0.5m/s,640*480的分辨率,视场为 4*3mm,3mm/480=0.006mm,因此像素当量为0.006mm
当物体在快门时间内的运动大于1.5个像素时我们就可以认为会出现拖影,因此要不出现拖影则:t(快门)=0.006*1.5/0.5=0.00018s
E.像元尺寸
像元尺寸=CCD宽/水平方向分辨率(或者 CCD高/垂直方向分辨率)
像元尺寸越大,感光效果越好

数字接口类型
USB : 120Mbps~480Mbps
1394a : 400Mbps
1394b : 800Mbps
GigE : 1000Mbps
CameraLink: (75MHz)
base 1.8Gbps
mediu 3.6Gbps
full 4.8Gbps
2. 镜头选型
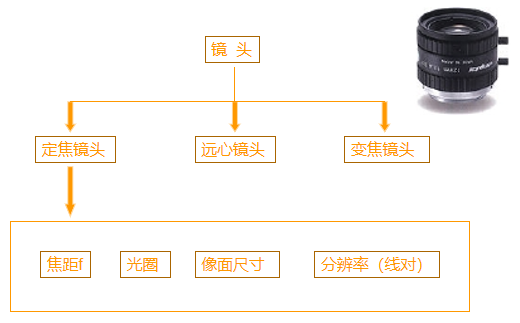
焦距f
f =工作距离* CCD高(宽) (物体高(宽)+CCD高(宽))
举例:物体大小80*80mm,工作距离200~300mm,采用1/2”CCD(宽6.4mm,高4.8mm )
则 F=WD*4.8/(80+4.8)=11.3~16.9mm,故选择 12mm镜头

光圈/相对孔径
A 概念:
a.相对孔径:孔径与焦距的比值(D/f)
b.光 圈:相对孔径的倒数。F = 1/(D/f)
B 分类:
a.手动
b.自动
分辨率(线对)
概念:在单位毫米内能够分辨开的黑白相间条纹数

分别率为1/2d, 其中d为线宽,分辨率的单位为lp/mm(线对/毫米)
例如一个CCD的像元尺寸大小为5um x 5um,则像元的分辨率为:
N=1/(2X0.005)=100(lp/mm)
在选择镜头时通常要求镜头的分辨率要略高于这个值。

景深公式为:
前景深 ΔL1=FδL²/f²+FδL
后景深 ΔL2= FδL²/f²-FδL
景深ΔL=ΔL1+ΔL2=2f²FδL²/f4 - F²δ²L²
由景深计算公式可以看出,景深与镜头使用光圈、镜头焦距、拍摄距离以及对像质的要求(表现为对容许弥散圆的大小)有关。
弥散圆的定义:
在焦点前后,光线开始聚集和扩散,点的影象变成模糊的,形成一个扩大的圆,这个圆就叫做弥散圆。
允许的最小弥散圆越大,景深越浅,推广到画幅上,就是在其它条件不变的情况下,画幅越大,景深越浅,画幅越小,景深越大。
允许弥散圆直径=感光元件对角线长度*1/1730。
相机与镜头之间的关系
举例:
客户现有一台½”相机(解析度752*582,像元大小为8.6um*8.3um)和一个镜头(镜头的分辨率为80lp/mm),由于相机停产,客户为节约成本,只想换相机而不换镜头,问该客户若换成¼”相机(解析度640*480,像元大小 5um* 5um )是否能满足要求?
客户原有½”相机所需镜头的分辨率(1/2d)=1/2*8.6*10-3=58lp/mm换成¼”相机后所需镜头的分辨率(1/2d) =1/2*5*10-3=100lp/mm根据选镜头时镜头的分辨率要大于计算出来的分辨率可知只换相机而只换镜头是达不到要求的。
成像质量对比:
1) VGA分辨率镜头所拍摄图像:

2) 百万像素分辨率镜头所拍摄图像:
3. 光源选型
条形光源

环形光源

背光源

点光源

同轴光源